|
isce3
0.1.0
|
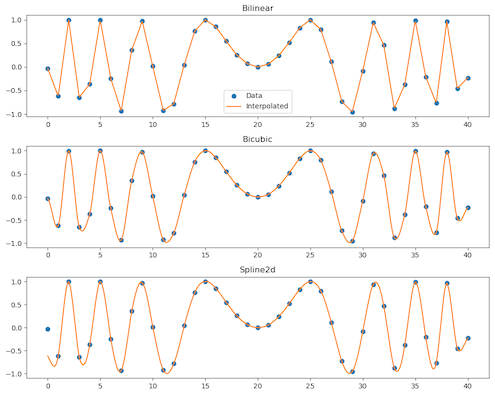
2D interpolation is a fundamental operation for image resampling, oversampling, terrain extraction, etc. ISCE currently implements several basic types of interpolation methods: bilinear, bicubic, spline, and sinc interpolation. For this example, we will test the first three interpolators on a synthetic low-resolution image.
We first generated a synthetic 2D low-resolution image which we wish to interpolate (this code follows the SciPy interp2d tutorial test data). The data are stored in an isce3::core::Matrix object which will be passed to all interpolation routines. Then, three different interpolators are created. Note that they are all instantiated as isce3::core::Interpolator pointers, which is the base class for all derived interpolator classes. The function isce3::core::createInterpolator takes as input an enum type that specifies the type of interpolation method we wish to use and then returns a pointer to the appropriate derived interpolation class. After creating vectors at which we want to perform the interpolation, we call each interpolator's interpolate() function. The plotted interpolation results are below:
 1.8.5.
1.8.5.